Have you ever spent your summer afternoons at home feeling the heat or wondering why your air conditioning is taking too long to kick in?
Well, here is a simple solution that can save us from feeling the heat indoors whilst also making energy and cost savings. - Insulation of walls!
Insulating (adding a layer or padding to) the walls of your home can reduce the air conditioning load by 20% and thereby reduce the amount of electricity consumed in a billing cycle, especially, during the summer months.
Why and how does insulation work?
Heat, unless interfered, naturally flows in one direction - from warm spaces toward cold spaces. This means that during winters, heat flows from inside your room to the outside. On the other hand, during summers,- heat flows from the outside to inside your room. This cannot be entirely avoided. But, adding a material layer to the walls can reduce the rate of the flow and provide adequate resistance to the flow of heat.
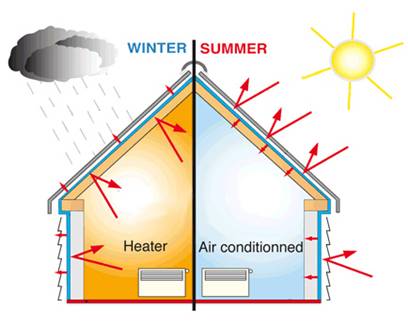
Source: How to insulate your home
Insulation can help maintain indoor temperature and minimise the impact of extreme heat or extreme cold in the house. It is also the first step towards improving the building design and making them naturally comfortable without pushing for more air-conditioning or heating.
Wall paint

Source: Canva
Adding insulating additives to your wall paint is one of the most efficient ways to insulate your wall. These additives are available in the market in the form of powders that can be mixed with paint to coat your walls with. Alternatively, there are a range of heat resistant insulation coatings (liquid/semi-liquid) that largely contain calcium silicate to ensure that your wall becomes a reflective, low-emittance surface.
Wallpaper

Source: Canva
There are decorative and eco-friendly wallpaper options for your indoor walls that can ensure insulation against heat, moisture and sound. These are made up of materials such as grass cloth, cotton fiber, cotton cellulose, paper products, cotton thread and other recycled materials.
Insulation boards

Source: Canva
If you have flat and clean internal walls, using easily attachable rigid insulation boards such as polystyrene or PIR boards could be the best heat resistant solution. These boards can be fixed onto the indoor walls with an adhesive and further covered with some finish like plasterboard, lath or plaster.
Stud wall and insulators
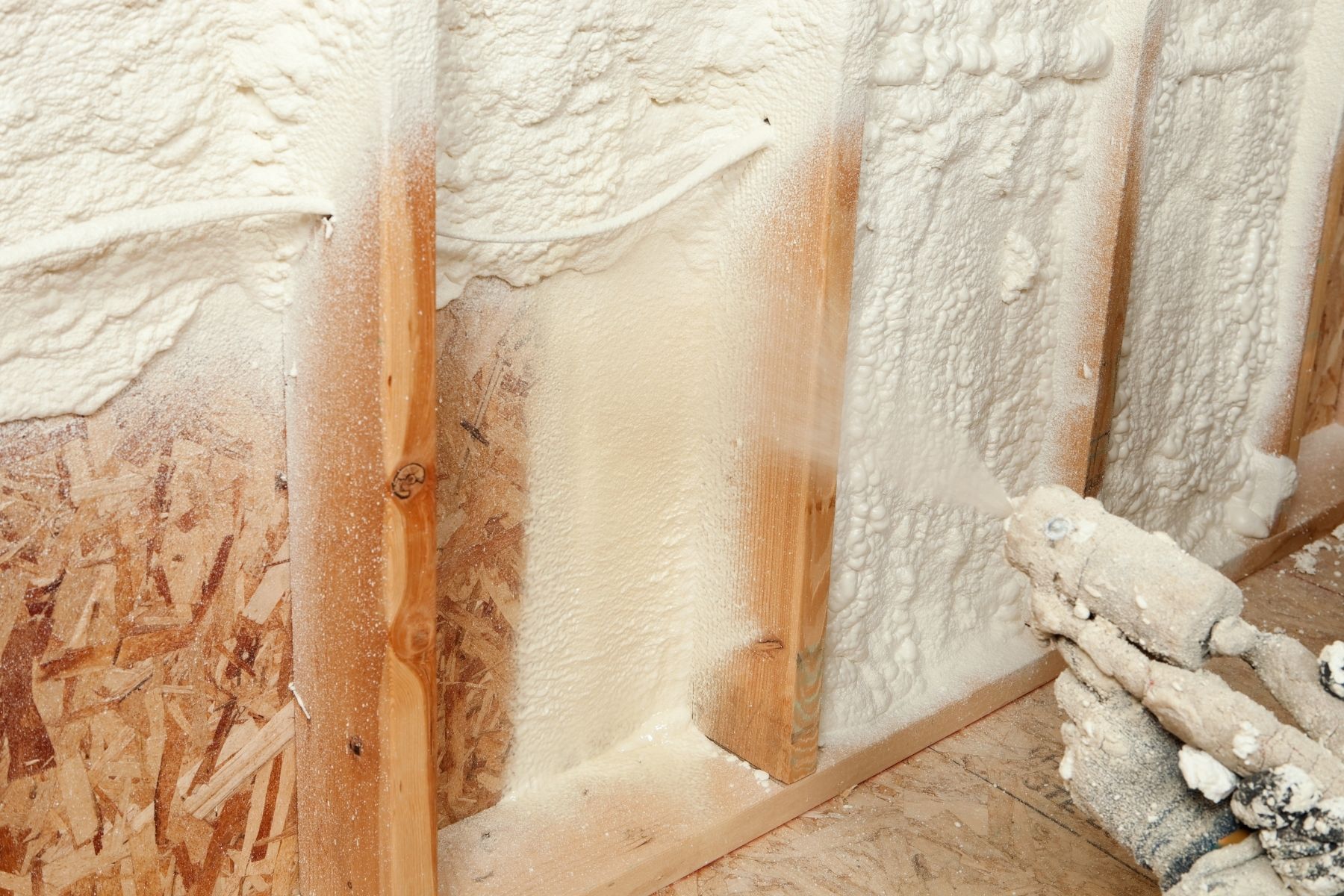

Source: Canva
A stud wall is the vertical framing in a building’s wall. Instead of using rigid insulation boards, a frame (made of timber or metal) that is filled with insulators can be added to your interior wall. There are a wide variety of insulators including natural fibres, mineral wool and recycled polyester, among others. Mineral wool is a highly effective insulating material and performs better than most other materials as it absorbs and releases moisture. Similar to insulation boards, stud walls with insulators can also be covered with some finish like plaster.
Living wall systems
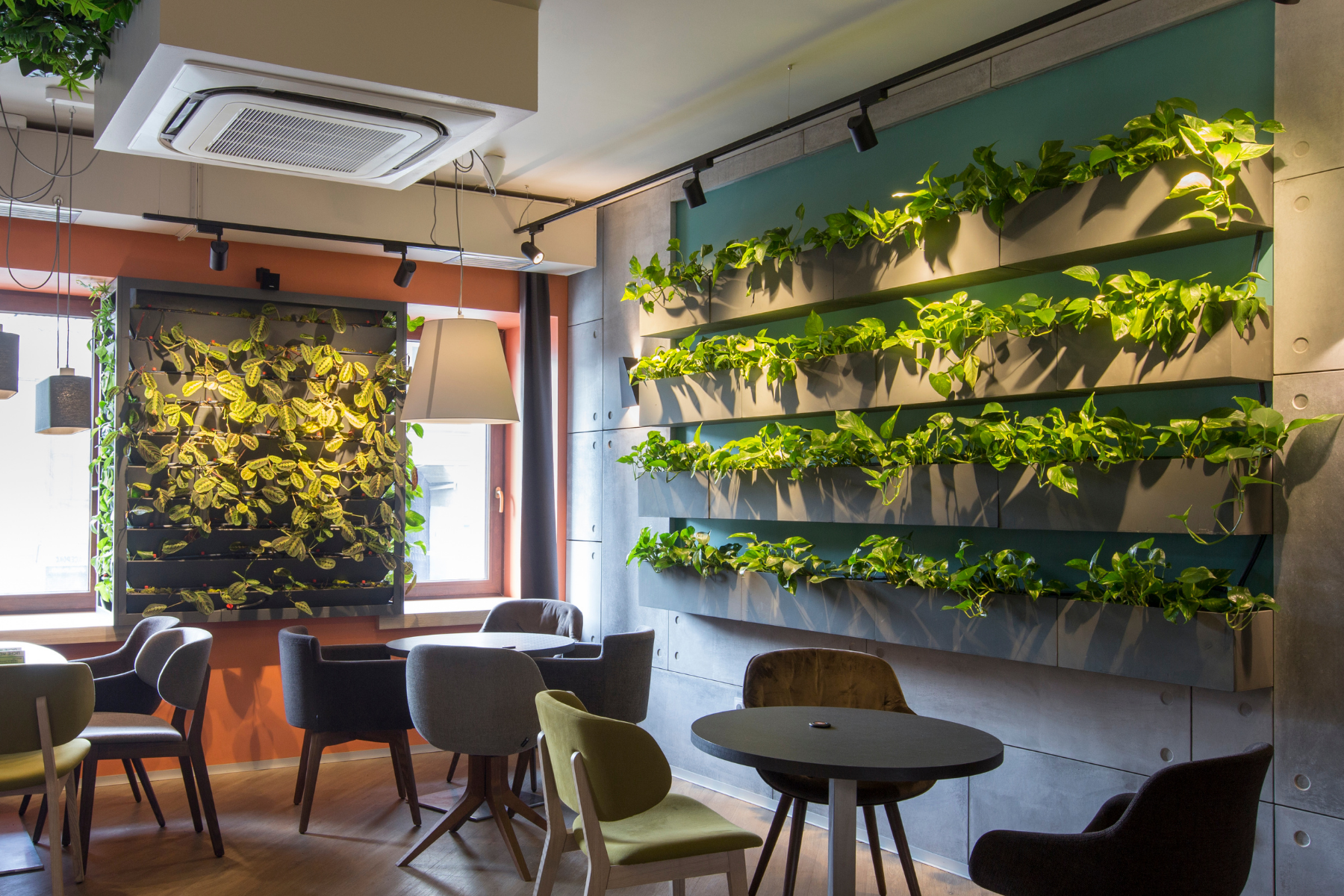

Source: Canva
Living wall systems are panels of plants, grown vertically on structures that can be either free-standing or attached to walls. Living wall systems are also known as vertical gardens, green walls, living walls or ecowalls. Studies reveal that installing such living wall systems can drastically reduce the need to cool the space, thus minimising the energy needs of the home.
Most of these wall insulation options are easy to adopt solutions that can result in increased energy and cost savings. This summer, insulate your walls and increase your savings!