Modern life is so separated from the source of food that we hardly know what we put into our bodies. Not only do we live far from farmlands, that we have lost our ancient connection to the soil, but the foods that we now eat are processed in so many ways that much of its resemblance to the original ingredients is lost. Labels then are the only way of identifying ingredients and obtaining information on what we eat. Food labels tell us what has gone into what we eat and whether it is safe for consumption.
The labelling, display and advertising of food products in India is regulated by the Food Safety and Standards Act, 2011 and 2018. This article will help you read a food label easily and make informed decisions about what you eat. Any food label should have mandatory information such as
-
brand name
-
food license
-
ingredients
-
quantity and weight
-
nutritional facts
-
logos for vegetarian/non-vegetarian food
-
manufacture date and expiry date (best before date, if the shelf life of the product is less than one week)
-
maximum retail price (MRP)
-
food certification mark
-
information about the manufacturer
-
caution/ advice for consumers
-
Avoid or limit food which has sugar components like dextrose, corn syrup, invert sugar, malt syrup, fructose, etc.;
-
Avoid or limit food which has salt components like sodium, sodium nitrates and nitrites, etc.;
-
Avoid artificial colours, food additives and preservatives 1;
-
Check for food allergens in food.

-
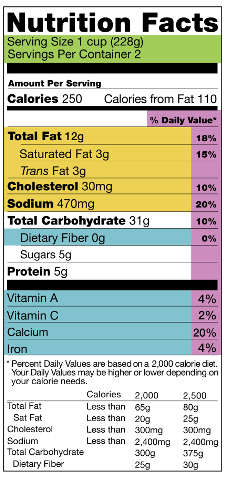
Serving size indicates how much of the food can be consumed in one meal at once and if the food package serves one or many. In this example, 1 serving size is 1 cup.
-
Calorie count is mentioned per serving and the calories needed per person will vary with different factors like age, gender, weight, activity level, health condition, etc 3. In this example, the consumer will gain 250 calories, of which 110 is from fats, from one serving.
-
Stay away from unhealthy fats like trans fats, saturated fats (3 grams each in this example), and partially hydrogenated oils.
-
It is preferable to select food products that contain good fats, like MUFA (Mono-Unsaturated Fatty Acid), PUFA (Poly-Unsaturated Fatty Acid), Omega 3-rich. (none in this example).
-
In this example, the consumer will get 31 grams of carbohydrates from one serving. Dietary fibres and sugars are also sources of carbohydrates and are included in this number. Dietary fibres do not increase our blood sugar - so a higher value in this is better than a higher value in sugars.
It is important to check the manufacturing/ expiry date and/or best before date. Sometimes, old stock is pushed to the front and new stock is placed at the back. In a hurry, we miss to read the label and consume expired products unknowingly which could lead to health issues. This can be avoided by reading the label 4 .
MRP: Checking the cost of food products irrespective of their brand is necessary to spend our money wisely.
Fruit Products Order (FPO) is a mandatory certification mark for processed fruit products like fruit jams, beverages, squashes, pickles, dehydrated fruits, fruit extracts, etc. The Ministry of Food Processing Industries develops the standards and issues the FPO.
FPO Logo
Agmark is a certification mark for agricultural products. Around 222 diverse commodities areunder agmark guidelines. Pulses, cereals, edible or vegetable oil, etc. Agmark is not a mandatory requirement and food labels having this logo are graded and marked by the Directorate of Marketing and Inspection, Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare.
AGMARK Logo
India Organic is a certification mark for organically produced farm products. It ensures that the raw materials used are organically produced without the use of chemical fertilizers, pesticides or plant hormones. This is voluntary and is issued by Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority (APEDA) under National Program for organic production of Government of India.
India Organic Logo
-
Additional nutritional information may be provided in the form of Barcode/Global Trade Identification Number (GTIN) 2.
-
On occasion of witnessing improper packaging, sale of expired product, no manufacturer address in the food label, etc, consumers can contact FSSAI through an online platform called ‘Food Safety Connect’ and register their complaints. They can also register complaints with the food safety officers in their respective states. Tamil Nadu Food Safety Department has published a whatsapp number - 94440 42322 for complaints.
-
Consumers can contact the Department of Consumer Affairs at the Centre through the National Consumer Helpline. In states, consumers may contact the State Helpline. For Tamil Nadu, the State Helpline number is 044-28592828
-
Consumers can also contact the Controller of the Department of Legal Metrology in each state and register complaints under Legal Metrology (Packaged Commodities) Rule 2011.
-
Consumers may also approach a registered consumer organisation for assistance
We come across instances where consumers fail to read the label and end up buying products without proper labels, at a higher price and/ or expired ones. As consumers, it is important for us to verify labels for necessary information before buying food products as it has a direct impact on our health.